pleural effusion cat ultrasound
Abdominal ultrasounds were performed in 70 cats with pleural effusion and revealed concurrent abdominal effusion in 59 of these cats. Effusion might be found more on one side than the.

An Ultrasound Pretender Atdove Org
Accumulation of fluid in the pleural space.

. Abdominal abnormalities identified on ultrasound included abdominal masses lymphadenopathy hepatic venous congestion hepatomegaly splenomegaly renal enlargement small intestinal wall thickening steatitis and pancreatitis. The lack of specificity is mainly due to. Pleural effusion is the abnormal accumulation of fluid in a cats chest cavity between the lungs and the lining of the chest pleura.
Traditional veterinary classification has distinguished between transudates modified transudates and exudates. Diagnostics will be necessary to confirm the cat has pleural effusion and determine a cause. Retrospective analysis of pleural effusion in cats CD and neoplasia were the most common causes for feline pleural effusion.
Normal fluid is clear and colorless to slightly yellow and is of low cellularity. Classification of pleural effusion PE is central to diagnosis. Major Differential Diagnoses for Pleural Effusion in the Cat.
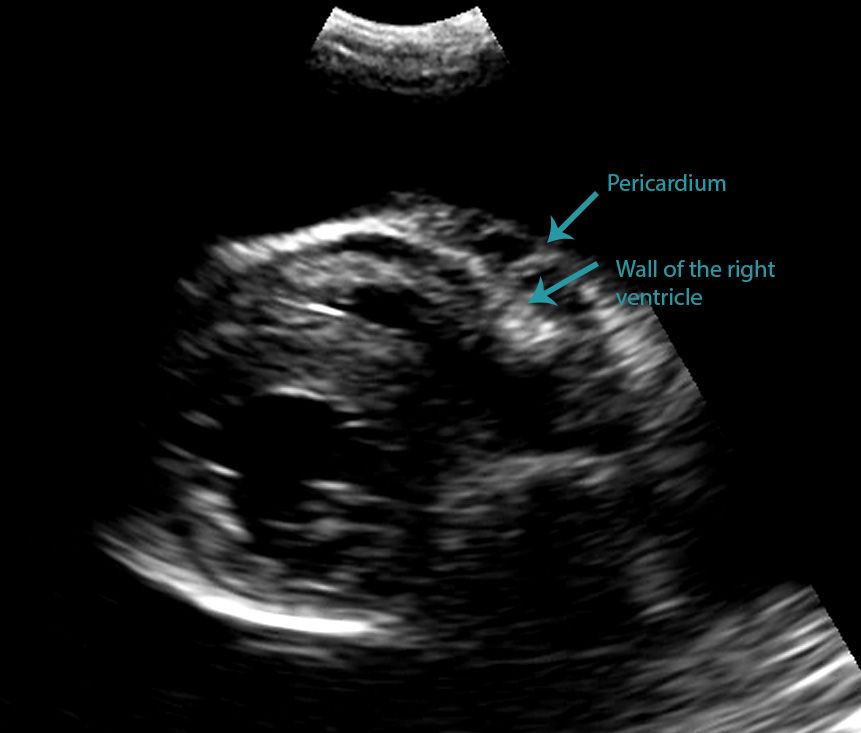
Volume 0365 b3 4529 b2 159723 b 88377. Unlike with a pericardial effusion in the case of accumulation of fluid in the pleural space there is no collapse of the heart walls. The type of pleural fluid withdrawn will enable your.
337 including the 5 who had no radiographic evidence of pleural. How i approach a cat with pleural effusion. A sample of pleural fluid obtained by piercing the cats chest cavity with a needle will be sent to the laboratory for analysis.
Very little or no fluid can be aspirated unless effusion is present. Of the cats that received thoracic ultrasound most exhibited bilateral pleural effusion 93. Where b maximum effusion depth.
Diverse disease processes result in sufficient fluid accumulation within the pleural space to cause respiratory compromise. Four standard effusion types recognized in addition to blood. Pleural Effusion Cat Ultrasound.
Pleural fluid occurs within the thoracic cavity. For those who are new to imaging around the heart with ultrasound differentiating. In pleural effusion the fluid is not found within the lungs but instead within the pleural sac.
The most commonly diagnosed cause of pleural effusion in cats is chylothorax. Pleural effusion refers to the abnormal accumulation of fluid within the chest cavity. The calculator uses the following formula originally published by Hazlinger et al.
Pleural effusion was confirmed in all of the cats who had thoracic ultrasonography 128380. Some affected cats may also cough. Cats with pleural effusion often have rapid shallow breathing and pet owners may notice increased respiratory effort.
Age liver enzymes as well as cell count protein and. Diverse disease processes result in sufficient fluid accumulation within the pleural space to cause respiratory compromise. Cats presenting with pleural effusion are nearly always in respiratory distress ranging from an increased respiratory rate and effort to open mouth breathing.
This review outlines a practical approach to cases of pleural effusion focusing on early recognition and confirmation of pleural space disease stabilisation of the patient and. Pleural effusion can be confirmed with radiography a single DV view if patient permits or thoracic ultrasonography. Determining the underlying aetiology is key to.
Focused Assessment Sonography for Trauma FAST procedure. Cats presenting for pleural effusion are often experiencing shortness of breath and decreased oxygen intake placing them into an oxygen cage provides some degree of. In the below clip from the Sonoscape S2.
Regardless of your level of experience with ultrasound ruling out pleural and pericardial effusions is essential. This can be caused by thoracic lymphangiectasia swollen lymph vessels that leak chyle into the pleural. Causes of Pleural Effusion in Cats Fluid builds up in the.
Pleural effusion is commonly used as a catch-all term to describe any abnormal accumulation of fluid in the pleural cavity. Additional findings in patients with pyothorax may include depression anorexia weight loss dehydration muffled heart and lung sounds and pale.

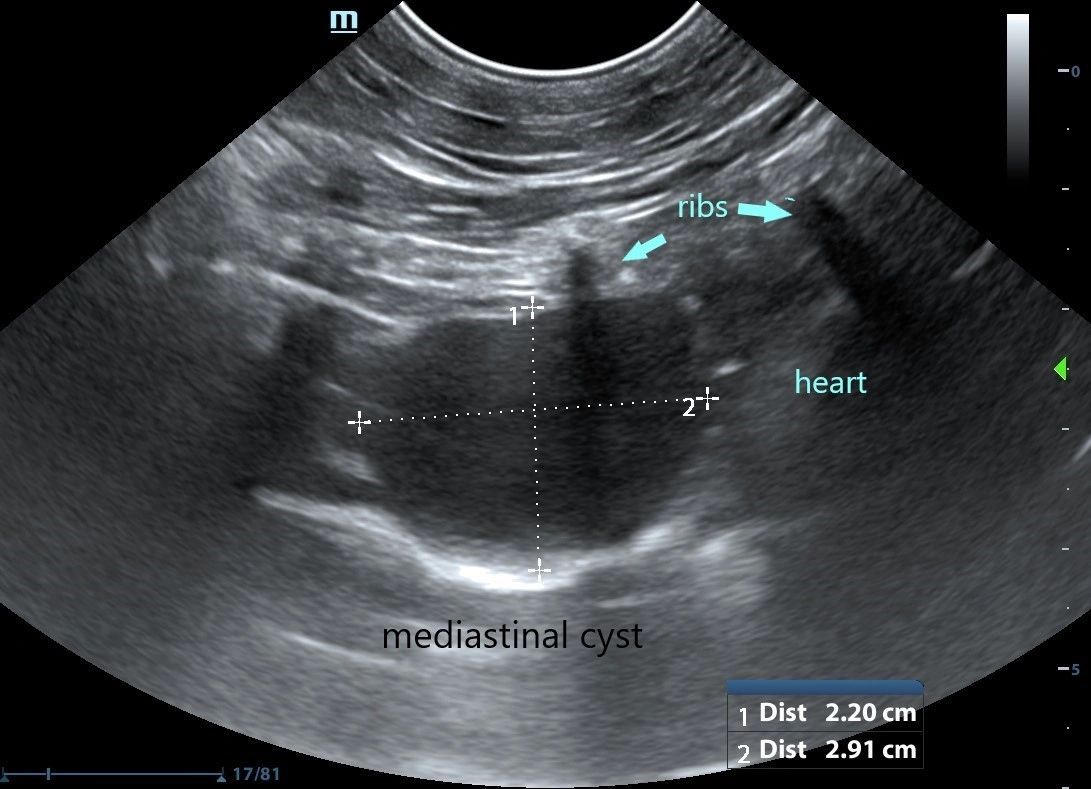
Differentiating Pericardial From Pleural Effusion Animal Ultrasound Association
Veterinary Ultrasound Diagnostic Imaging Clinical Images Search Esaote
Veterinary Echocardiography Newsletter 1 Effusions Animal Ultrasound Association
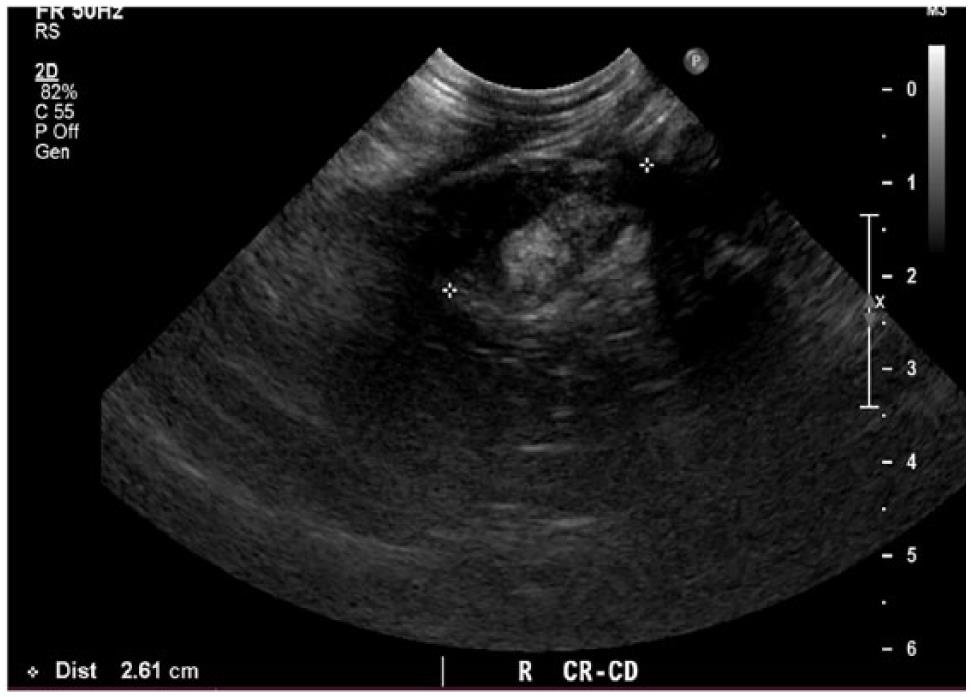
Spontaneous Cholecystopleural Fistula Leading To Biliothorax And Sepsis In A Cat
Lung Ultrasound Flooding In Fulminant Pulmonary Oedema In Cats And A Comparison With Pneumonia Vet Practice Support

Veterinary Echocardiography Newsletter 1 Effusions Animal Ultrasound Association

Differentiating Pericardial From Pleural Effusion Animal Ultrasound Association

How To Ultrasound Detection Of Pleural Fluid Case Study Video Youtube

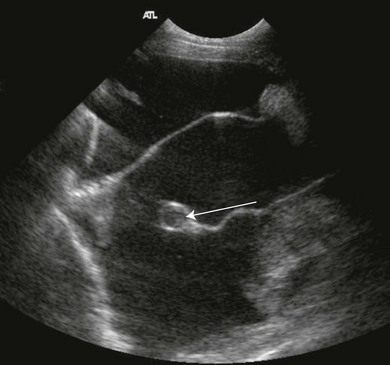
Cat Of Figure 1 Thoracic Ultrasound Revealed A Mild Hypoechoic Download Scientific Diagram
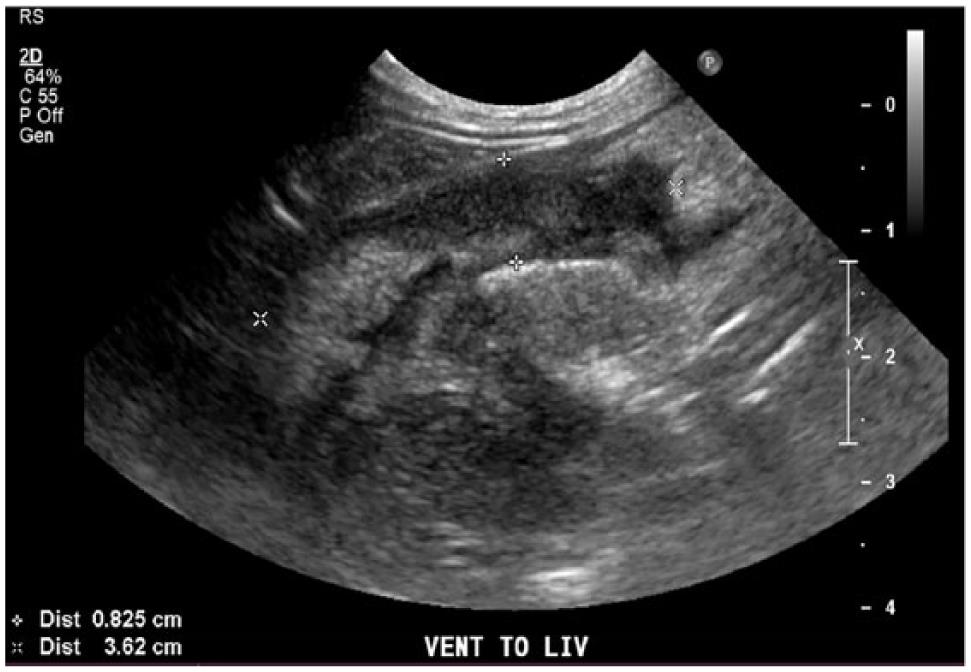
Spontaneous Cholecystopleural Fistula Leading To Biliothorax And Sepsis In A Cat

Pleural Effusion In A Cat Ultrasound Fip Youtube

Pdf Thoracic Ultrasound A Method For The Work Up In Dogs And Cats With Acute Dyspnea Semantic Scholar

Lung Ultrasound Fundamentals Wet Versus Dry Lung Signs Of Consolidation In Dogs And Cats Veterinary Clinics Small Animal Practice
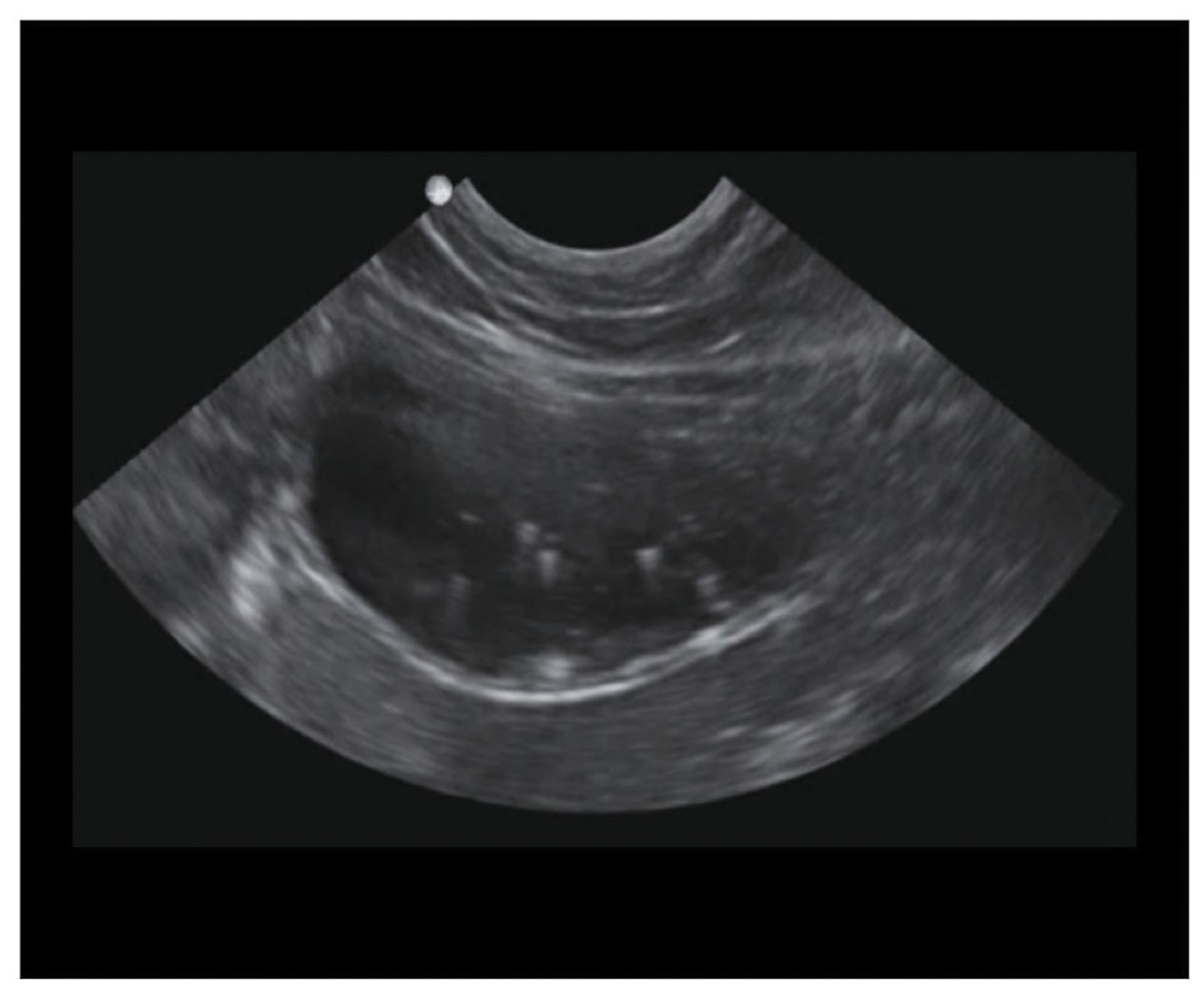
Front Line Ultrasound Imaging Of The Feline Urinary

Pdf Thoracic Ultrasound A Method For The Work Up In Dogs And Cats With Acute Dyspnea Semantic Scholar

Focused Ultrasound Of Superficial Soft Tissue Swellings Masses And Fluid Collections In Dogs And Cats Veterinary Clinics Small Animal Practice